Mark Poynting,Local weather Reporter
The US climate company NOAA has warned that the North Atlantic might expertise seven main hurricanes of class three or better this 12 months, double the same old quantity.
Usually you’ll count on three main hurricanes in a season.
13 Atlantic hurricanes of class one or larger are forecast for the interval from June to November.
Report excessive sea floor temperatures are partly accountable, as is a possible shift in regional climate patterns.
Though there isn’t a proof that local weather change is inflicting extra storms, it’s creating extra highly effective storms, and bringing heavier rainfall.
“This (hurricane) season is anticipated to be a unprecedented one,” NOAA Administrator Rick Spinrad mentioned at a information convention.
The The recent weakening of the El Nino weather pattern – and presumably a change to La Niña situations later within the 12 months – creates extra favorable atmospheric situations for these storms within the Atlantic.
In contrast to the Atlantic, NOAA had already predicted a “Below Normal” Hurricane Season Within the central Pacific area, the place the transition to La Niña has the alternative impact.
On common, the Atlantic basin—which incorporates the Atlantic Ocean, Caribbean Sea, and Gulf of Mexico—experiences 14 named tropical storms a 12 months, of which seven are hurricanes and three are main hurricanes.
Tropical storms change into hurricanes after they attain excessive sustained wind speeds of 74mph (119km/h). ‘Main’ hurricanes (class three and above) are those who attain a minimum of 111mph (178km/h).
In complete NOAA expects between 17 and 25 named tropical storms, of which between eight and 13 might change into hurricanes and between 4 and 7 might change into main.
Essentially the most main hurricanes in an Atlantic season is seven, seen in each 2005 and 2020. NOAA’s forecast means that 2024 might come shut.
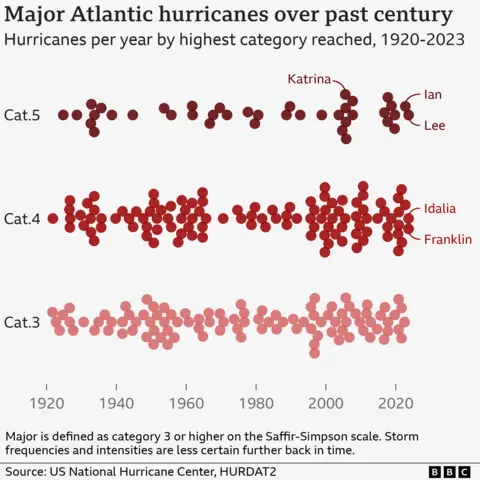
The precise causes of particular person storms are complicated, however there are two fundamental elements behind the forecast.
First, the transition from El Nino to La Nina is probably going within the coming months, which helps these storms develop extra simply.
And second, sea floor temperatures are a lot hotter than regular in the primary storm improvement area within the tropical Atlantic.
This usually means extra highly effective hurricanes, as hotter water offers storms extra power to develop as they monitor west.
Ken Graham, director of the US Nationwide Climate Service, mentioned “all the weather are in place” for intense hurricane season.
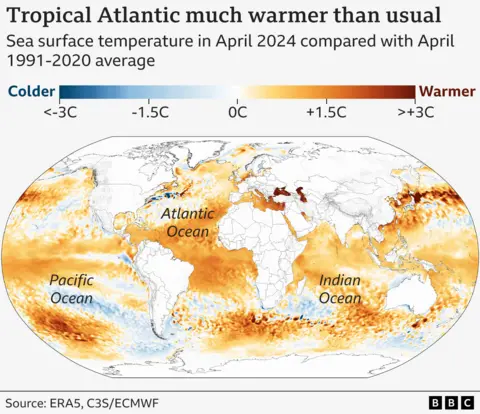
To attract consideration to the best way through which world warming is rising the chance of hurricanes of the best depth, A recent study Explored the opportunity of creating a brand new class of six ranges.
“It should alert the general public that essentially the most highly effective tropical cyclones we’re experiencing now are unprecedented and (are) as a consequence of floor oceans as a consequence of local weather change,” explains Michael Wehner, a senior scientist at Berkeley Earth and lead writer of the examine. “Being heat”.
Hurricane classes solely take wind pace into consideration. However these storms pose different main hazards, akin to rainfall and coastal flooding, that are usually getting worse with local weather change, NOAA warns.
Hotter air can maintain extra moisture, rising rainfall depth.
Throughout this time The storm rises – Quick-term rise in sea degree from storms – now occurring on prime of excessive base. It’s because sea ranges at the moment are larger, primarily as a consequence of melting glaciers and hotter oceans.
“Sea-level rise will increase complete flood depth, making right this moment’s storms extra damaging than final 12 months’s storms,” says Andrew Dessler, professor of atmospheric sciences at Texas A&M College.
Given the energetic forecast, researchers harassed the necessity for the general public to pay attention to the risks of those storms — particularly in “excessive depth occasions,” the place the storm’s wind speeds enhance in a short time. , and thus could be notably harmful.
“We’re already seeing an total enhance within the quickest charges at which Atlantic hurricanes intensify — which implies we’re probably seeing an elevated danger of hazard to our coastal communities,” Rowan within the U.S. explains Andrea Garner, an assistant professor on the college.
“The fast intensification of hurricanes can nonetheless be troublesome to foretell, which in flip will increase the challenges that come up when making an attempt to guard our coastal communities.”
Graphics by Irwan Rivalt and Muskin Lider


